Introduction
Edges belong to the graph data. In g6R, edges can be created from a dataframe or a list such as:
edges <- data.frame(
source = c(1, 2),
target = c(2, 3)
)While the former might be more convenient for simple cases, the latter provides more flexibility for advanced customization since some edge properties have to be nested lists, for instance style properties:
edges <- list(
list(
source = "1",
target = "2",
style = list(
...
)
),
list(
source = "2",
target = "3",
style = list(
...
)
)
)In g6R, the preferred way to create edges is by using
the helper functions g6_edge() and
g6_edges().
These functions provide a consistent and user-friendly interface for
edge creation, supporting both simple and advanced customization.g6_edge() allows you to define a single edge with specific
properties, while g6_edges() and as_g6_edges()
can generate multiple edges from various input formats (data.frame,
list):
as.list(methods("as_g6_edge"))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "as_g6_edge.g6_edge"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "as_g6_edge.list"
as.list(methods("as_g6_edges"))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "as_g6_edges.data.frame"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "as_g6_edges.g6_edges"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "as_g6_edges.list"Using these helpers ensures compatibility with all g6R features and is the recommended method for edge creation.
For example:
# Create a single edge
edge <- g6_edge(source = "A", target = "B", type = "line", style = list(stroke = "blue"))
# Create multiple edges from a data frame
df <- data.frame(source = c("A", "B"), target = c("B", "C"), type = c("line", "cubic"))
edges <- as_g6_edges(df)
# With g6_edges()
edges <- g6_edges(
g6_edge(source = "A", target = "B", type = "line"),
g6_edge(source = "B", target = "C", type = "cubic")
)
# with a list
lst <- list(
list(source = "A", target = "B", type = "line"),
list(source = "B", target = "C", type = "cubic")
)
edges <- as_g6_edges(lst)
edges
#> [[1]]
#> $source
#> [1] "A"
#>
#> $target
#> [1] "B"
#>
#> $id
#> [1] "A-B"
#>
#> $type
#> [1] "line"
#>
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "g6_edge" "g6_element"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> $source
#> [1] "B"
#>
#> $target
#> [1] "C"
#>
#> $id
#> [1] "B-C"
#>
#> $type
#> [1] "cubic"
#>
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "g6_edge" "g6_element"
#>
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "g6_edges"Data properties
g6R edges are allowed to have the following properties:
-
source: the id of the source node, required. -
target: the id of the target node, required. -
id: a unique identifier for the edge (optional, if not passed it will be<source>-<target>). -
type: the type of the edge. -
data: custom data for the edge that can be retrieved. -
style: style properties. A comprehensive list is available here. -
states: initial states. An unnamed list of valid states.
Edge types
Builtin types are line, polyline,
quadratic, cubic:
types <- c(
"line",
"polyline",
"quadratic",
"cubic"
)
nodes <- data.frame(id = as.character(1:5))
edges <- lapply(seq_along(types), \(i) {
list(
source = 1,
target = i + 1,
id = types[[i]],
type = types[[i]],
style = list(
labelText = types[[i]]
)
)
})
g6(nodes, edges) |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())Special type cubic-vertical and
cubic-horizontal are respectively used for vertical and
horizontal layouts:
tree$nodes$label <- NULL
g6(tree$nodes, tree$edges) |>
g6_layout(dendrogram_layout(nodeSep = 36, rankSep = 250, direction = "LR")) |>
g6_options(edge = list(type = "cubic-horizontal"), autoFit = "view")Special types
g6R implements a custom type with animation, namely
fly-marker-cubic. This type has been implemented with
JavaScript code and registered in the g6R package. You may
do the same for your own custom types.
nodes <- data.frame(id = 1:2)
edges <- list(
list(
source = 1,
target = 2,
type = "fly-marker-cubic"
)
)
g6(nodes, edges, height = "200px") |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())Styling edges
The g6 JavaScript library exposes a wide range of style
properties for edges, which can be set in the style
property of the edge data. We list below the most outstanding
properties, but you can find a comprehensive list in the documentation.
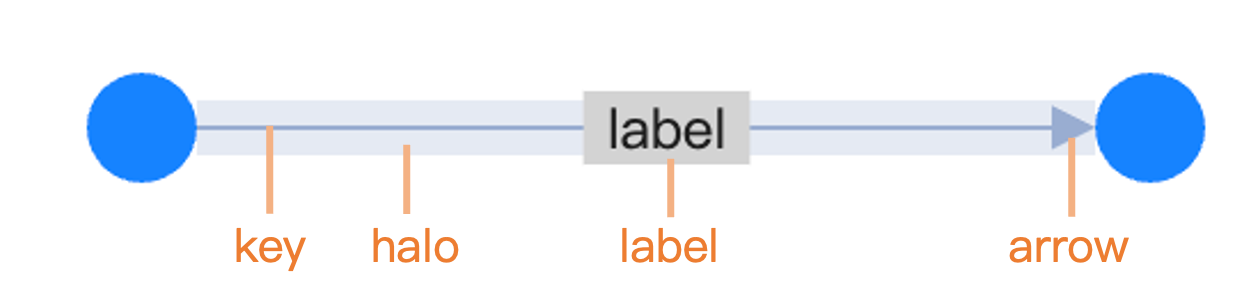
Main graphic properties
These properties are used to define the main graphic style of the edge, such as color, width, and line type. Like for nodes, these options may be set either at the global edge option level or at the individual edge level. Here is an example of how to set the color for a given edge:
nodes <- data.frame(id = 1:2)
edges <- list(
list(
source = 1,
target = 2,
style = list(
stroke = "pink",
lineWidth = 10
)
)
)
g6(nodes, edges, height = "200px") |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())Label styling
Some common properties include label styling:
nodes <- data.frame(id = 1:2)
edges <- list(
list(
source = 1,
target = 2,
style = list(
labelText = "Edge Label", # Label text content
labelFill = "blue", # Label text color
labelOffsetY = 20, # Vertical offset of the label
labelFontSize = 14, # Label font size
labelPlacement = "center", # Position of the label relative to the edge,
labelBackground = TRUE, # Whether to display the label background
labelBackgroundFill = "yellow" # Background color of the label
)
)
)
g6(nodes, edges, height = "200px") |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())Badges
You can add badges
to edges using the badge property in the style
list. Badges are small indicators that can display additional
information, such as counts or statuses:
nodes <- data.frame(id = 1:2)
edges <- list(
list(
source = 1,
target = 2,
style = list(
labelText = "Edge Label", # Label text content
labelFill = "blue", # Label text color
labelFontSize = 14, # Label font size
labelOffsetY = 20, # Vertical offset of the label
labelPlacement = "center", # Position of the label relative to the edge,
badgeText = "badge", # Edge badge text
badgeFill = "green", # Edge badge text color
badgeOffsetX = -40, # Edge badge offset in the x-axis direction
badgePlacement = "suffix", # Position of the badge relative to the edge
badgeBackground = TRUE # Enable edge badge background
)
)
)
g6(nodes, edges, height = "200px") |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())Arrow styling
End and start arrows can be styled too:
nodes <- data.frame(id = 1:2)
edges <- list(
list(
source = 1,
target = 2,
style = list(
startArrow = TRUE, # Enable edge start arrow
startArrowFill = "yellow", # Edge start arrow fill color
startArrowType = "rect", # Edge start arrow type
endArrow = TRUE, # Enable edge end arrow
endArrowFill = "orange", # Edge end arrow fill color
endArrowType = "triangle" # Edge end arrow type
)
)
)
g6(nodes, edges, height = "200px") |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())States
Edges can have different states
that can be used to indicate different conditions or interactions.
States can be set in the states property of the edge
data:
states <- c(
"default",
"selected",
"highlight",
"active",
"inactive",
"disabled"
)
nodes <- data.frame(id = 1:7)
edges <- lapply(seq_along(states), \(i) {
list(
source = 1,
target = i + 1,
states = list(states[[i]]),
style = list(
labelText = states[[i]]
)
)
})
g6(nodes, edges) |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout())Color palette
One can assign a color palette
for edges such that they may be grouped given a specific property. In
the following, we use the “Les Misérables” dataset, which contains edges
and a value column, for which we set a color palette. There
are length(unique(lesmis$edges$value)) color choices:
edges <- unname(split(lesmis$edges, seq(nrow(lesmis$edges))))
edges <- lapply(edges, function(edge) {
list(
source = edge$source,
target = edge$target,
data = edge$data[[1]]
)
})
g6(lesmis$nodes, edges) |>
g6_layout(d3_force_layout()) |>
g6_options(
animation = FALSE,
autoFit = "view",
autoResize = TRUE,
edge = list(
style = list(endArrow = TRUE),
palette = list(
type = "group", # use discret palette
field = "value", # The property to group edges by
color = "tableau"
)
)
)Update edges data
These functions can only be used in a Shiny app context. They allow you to get or update the edges data in the graph after it has been created. The functions are:
-
g6_add_edges(): adds new edges to the graph. -
g6_update_edges(): updates existing edges in the graph. -
g6_remove_edges(): removes edges from the graph. -
g6_set_edges(): set edges state. -
g6_get_edges(): get edges data from the graph.
We provide more details and examples in the Shiny integration vignette.